Python Program to Flatten a Nested List using Recursion
This Python program flattens a nested list using recursion.Flattening a nested list refers to the process of converting a list that contains sub lists (which can themselves contain sub lists) into a single, one-dimensional list. This transformation simplifies the structure by removing any levels of nesting. To achieve this using recursion, we implement a function that iterates through each element of the list.
Problem Statement
You are given a nested list that contains integers and sub lists. Your task is to write a Python function to flatten the nested list using recursion and return a single, one-dimensional list containing all the elements.
Python Program to Flatten a Nested List using Recursion
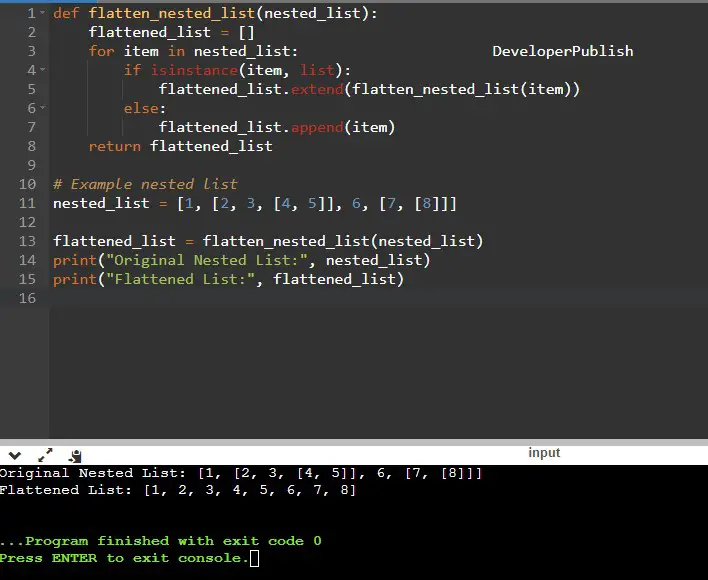
def flatten_nested_list(nested_list):
flattened_list = []
for item in nested_list:
if isinstance(item, list):
flattened_list.extend(flatten_nested_list(item))
else:
flattened_list.append(item)
return flattened_list
# Example nested list
nested_list = [1, [2, 3, [4, 5]], 6, [7, [8]]]
flattened_list = flatten_nested_list(nested_list)
print("Original Nested List:", nested_list)
print("Flattened List:", flattened_list)
How it Works
- Initial Call: The
flatten_nested_listfunction is called with the initial nested list[1, [2, 3, [4, 5]], 6, [7, [8]]]. - Iteration 1: The function enters the loop and encounters the first item, which is
1. Since it’s not a list, it’s directly added to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list:[1] - Iteration 2: The function moves to the next item, which is
[2, 3, [4, 5]]. This is a sublist, so the function enters a recursive call with this sublist. - Recursive Call: Now the function is called with the sublist
[2, 3, [4, 5]].- Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
2, which is not a list. It’s added to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list(inside recursion):[2] - Iteration 2 (Recursive): The function encounters
3, another non-list item, and adds it to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list(inside recursion):[2, 3] - Iteration 3 (Recursive): The function encounters
[4, 5], which is a sublist. A new recursive call is made with this sublist.
- Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
- Recursive Call: The function is now called with the sublist
[4, 5].- Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
4(non-list) and adds it to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list(inside deeper recursion):[4] - Iteration 2 (Recursive): The function encounters
5(non-list) and adds it to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list(inside deeper recursion):[4, 5]
[4, 5]is returned back to the previous level of recursion. - Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
- Back to Previous Level (Recursive): The result
[4, 5]is received from the deeper recursion and added to theflattened_listof the current level of recursion.Currentflattened_list(inside recursion):[2, 3, 4, 5] - Recursive Call Finished: The recursion for the sublist
[2, 3, [4, 5]]is complete, and the result[2, 3, 4, 5]is returned back to the original level of recursion. - Back to Original Level: The result
[2, 3, 4, 5]is received from the recursive call and added to theflattened_listof the original call.Currentflattened_list:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] - Iteration 3: The function encounters
6(non-list) and adds it to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] - Iteration 4: The function encounters
[7, [8]], a sublist. Another recursive call is made with this sublist. - Recursive Call: The function is now called with the sublist
[7, [8]].- Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
7(non-list) and adds it to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list(inside recursion):[7] - Iteration 2 (Recursive): The function encounters
[8], a sublist. A new recursive call is made.
- Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
- Recursive Call: The function is called with the sublist
[8].- Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
8(non-list) and adds it to theflattened_list.Currentflattened_list(inside deeper recursion):[8]
[8]is returned back to the previous level of recursion. - Iteration 1 (Recursive): The function encounters
- Back to Previous Level (Recursive): The result
[8]is received from the deeper recursion and added to theflattened_listof the current level of recursion.Currentflattened_list(inside recursion):[7, 8] - Recursive Call Finished: The recursion for the sublist
[7, [8]]is complete, and the result[7, 8]is returned back to the original level of recursion. - Back to Original Level: The result
[7, 8]is received from the recursive call and added to theflattened_listof the original call.Currentflattened_list:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] - Flattening Complete: The iteration through the input list is complete, and the final
flattened_listis returned. - Print Results: The program prints both the original nested list
[1, [2, 3, [4, 5]], 6, [7, [8]]]and the flattened list[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8].
Input/ Output




Leave a Review