Python Program to Reverse a Linked List without Recursion
In this Python program, we will reverse a linked list without using recursion. We’ll implement a non-recursive approach to reverse the order of elements in a singly linked list.
Problem Statement
Given a singly linked list, you need to reverse the order of its elements without using recursion.
Python Program to Reverse a Linked List without Recursion
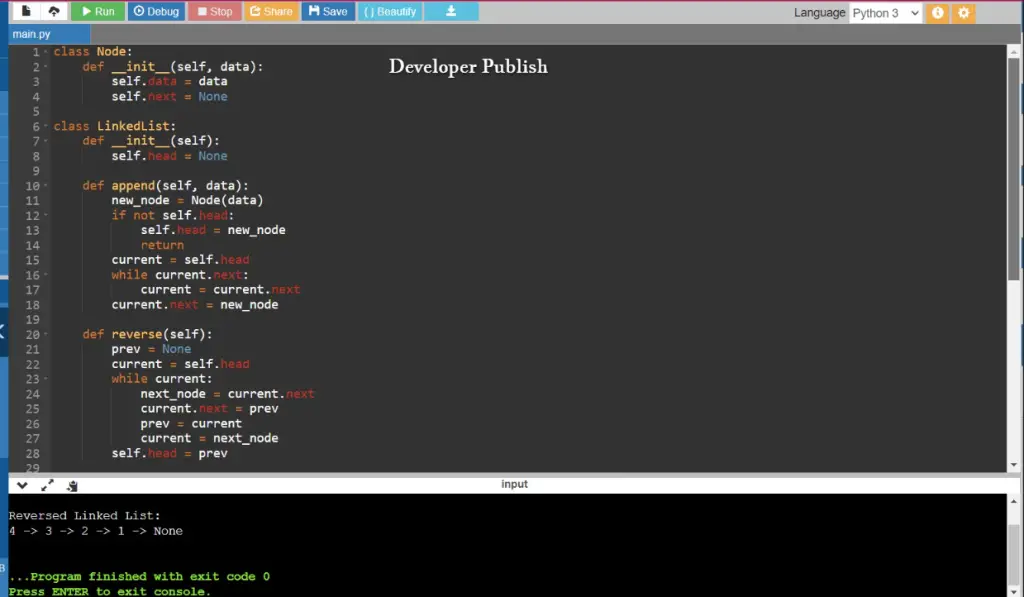
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def reverse(self):
prev = None
current = self.head
while current:
next_node = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = next_node
self.head = prev
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" -> ")
current = current.next
print("None")
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.append(1)
linked_list.append(2)
linked_list.append(3)
linked_list.append(4)
print("Original Linked List:")
linked_list.display()
linked_list.reverse()
print("\nReversed Linked List:")
linked_list.display()
How It Works
- The
Nodeclass defines the individual elements of the linked list with a data attribute and a reference to the next node. - The
LinkedListclass contains methods for appending elements, reversing the list, and displaying the list. - The
appendmethod adds elements to the end of the linked list. - The
reversemethod iterates through the list, updating thenextreferences to reverse the connections between nodes. - The
displaymethod prints the elements of the linked list.
Input/Output




Leave a Review