C Program to Perform Addition using Bitwise Operators
This C program demonstrates addition using bitwise operators. Bitwise operators are efficient for performing arithmetic operations at the binary level.
Bitwise operators in C are used to manipulate individual bits of data at the binary level. These operators work on the individual bits of operands, performing operations such as AND, OR, and XOR, and shifting bits left or right. One common application of bitwise operators is performing arithmetic operations, such as addition, using only these operators.
Problem Statement
Your program should define a function called bitwiseAdd that takes two integer parameters and returns the sum. The addition should be performed using bitwise operators only, without using the conventional addition operator (+).
The program should have the following specifications:
- The program should prompt the user to enter two integers.
- It should call the
bitwiseAddfunction with the input values. - The
bitwiseAddfunction should implement the addition using bitwise operators. - The sum calculated using bitwise operations should be returned by the
bitwiseAddfunction. - The program should then print the resulting sum.
Note: Assume that the input integers are non-negative.
Example:
Enter two numbers: 5 3
Sum: 8
In the above example, the user enters the numbers 5 and 3. The program performs the bitwise addition operation and calculates the sum as 8 using the bitwiseAdd function. Finally, it prints the sum as the output.
Your task is to implement the bitwiseAdd function and the main program logic to solve the problem.
C Program to Perform Addition using Bitwise Operators
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int carry = a & b;
a = a ^ b;
b = carry << 1;
}
return a;
}
int main() {
int num1, num2, sum;
printf("Enter two numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
sum = add(num1, num2);
printf("Sum: %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
How it Works
The program works by implementing addition using bitwise operators. It takes two integers as input and performs the addition operation without using the conventional addition operator (+). Here’s how it works:
- The program prompts the user to enter two integers.
- The
scanffunction is used to read the input values and store them in variablesnum1andnum2. - The program then calls the
bitwiseAddfunction, passing the input valuesnum1andnum2. - Inside the
bitwiseAddfunction, a while loop is used to continue the addition until there is no carry left. - In each iteration of the while loop, the bitwise AND operator
&is used to calculate the carry. The carry is obtained by performing a bitwise AND operation betweenaandb. - The bitwise XOR operator
^is used to calculate the sum without the carry. The sum is obtained by performing a bitwise XOR operation betweenaandb. - The carry is then shifted to the left by one position using the left shift operator
<<. This prepares the carry for the next iteration. - The updated values of
sumandcarryare assigned back toaandb, respectively. - The while loop continues until there is no carry left (i.e.,
bbecomes 0). - Finally, the function returns the calculated sum.
- Back in the
mainfunction, the returned sum is stored in thesumvariable. - The program then prints the resulting sum using the
printffunction.
By using bitwise operators and the concept of binary addition, the program effectively performs addition without using the conventional addition operator.
Input /Output
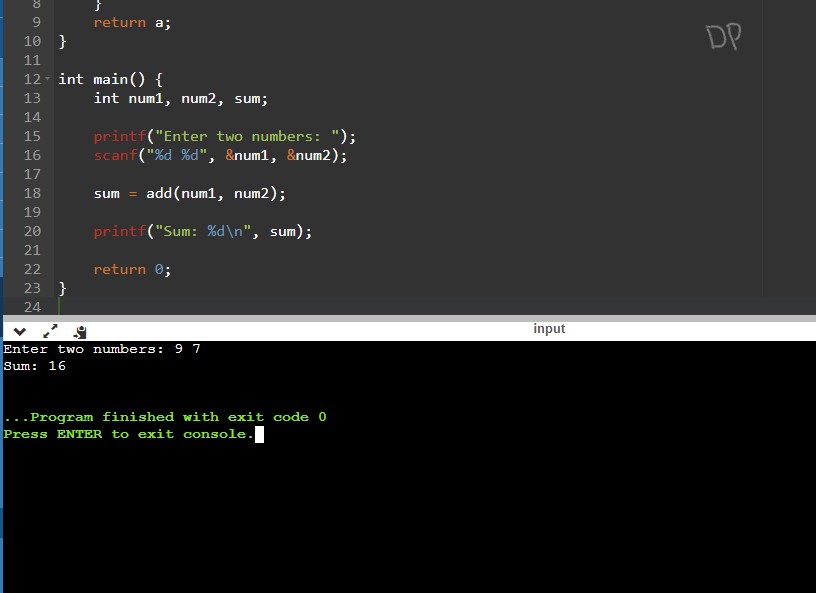
In this example, the user enters the numbers 9 and 7. The program performs the bitwise addition operation and calculates the sum as 16 using the bitwiseAdd function. Finally, it prints the sum as the output.

Leave a Review