C Program to Calculate the Value of sin(x)
This C program calculates the value of sin(x) using the Taylor series expansion. The Taylor series expansion is a mathematical series that represents a function as an infinite sum of terms. In this case, we use the Taylor series for sine to approximate the sine of a given angle (in radians).
The sine function is a fundamental trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. In mathematics, the sine function is typically defined using a series expansion known as the Taylor series.
Program Statement
Write a C program that calculates the value of sin(x) using the Taylor series approximation. The program should prompt the user to enter the value of the angle x in radians and the number of terms n to include in the series. The program should then calculate the approximated value of sin(x) using the Taylor series expansion and print the result to the console.
C Program to Calculate the Value of sin(x)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
double calculateSin(double x, int terms) {
double radians = x * (M_PI / 180.0);
double result = radians; // First term of the Taylor series
for (int i = 1; i <= terms; i++) {
double numerator = pow(-1, i) * pow(radians, 2 * i + 1);
double denominator = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= 2 * i + 1; j++) {
denominator *= j;
}
result += numerator / denominator;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
double angle;
int numTerms;
printf("Enter the angle in degrees: ");
scanf("%lf", &angle);
printf("Enter the number of terms to approximate: ");
scanf("%d", &numTerms);
double sinValue = calculateSin(angle, numTerms);
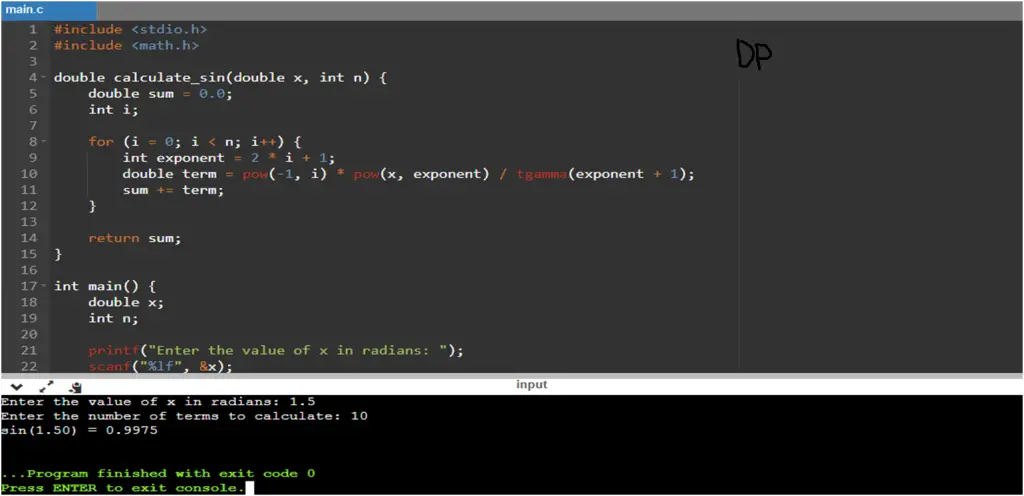
printf("The sin(%lf) is approximately %lf\n", angle, sinValue);
return 0;
}
How it works
- The program starts by including the necessary header files:
stdio.hfor input/output operations andmath.hfor mathematical functions likepowandtgamma. - The
calculate_sinfunction is defined, which takes two parameters:x(the angle in radians) andn(the number of terms to include in the series). This function calculates the value of sin(x) using the Taylor series expansion. It initializes a variablesumto store the cumulative sum of the terms. - Inside the
calculate_sinfunction, aforloop is used to iterate from 0 ton-1. Each iteration calculates a term of the Taylor series and adds it to thesum. The exponent of the term is calculated as2 * i + 1, and the term itself is calculated using the formulapow(-1, i) * pow(x, exponent) / tgamma(exponent + 1). Thepowfunction raises-1to the power ofiandxto the power of the exponent. Thetgammafunction calculates the factorial of the exponent (exponent + 1) to be used as the denominator of the term. - The
calculate_sinfunction returns the final value ofsum, which represents the approximated value of sin(x) based on the Taylor series expansion. - In the
mainfunction, the program prompts the user to enter the value ofx(the angle in radians) and reads it usingscanf. Similarly, it prompts the user to enter the number of termsnand reads it as well. - The program calls the
calculate_sinfunction, passing the values ofxandn, and stores the result in the variablesin_x. - Finally, the program uses
printfto display the result to the console, showing the value ofx, the calculated value of sin(x), and a message indicating the result is an approximation.
That’s a high-level overview of how the C program works. It takes the user inputs, calculates the approximated value of sin(x) using the Taylor series expansion, and displays the result.
Input/Output

Leave a Review