Python Program to Implement Stack using Queue
In this Python program, we’ll be implementing a stack using two queues. The stack data structure follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle, while queues follow the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle. By using two queues cleverly, we can mimic the behavior of a stack.
Problem Statement
Implement a stack data structure using two queues (queue1 and queue2) and provide methods to push, pop, and check if the stack is empty (is_empty).
Python Program to Implement Stack using Queue
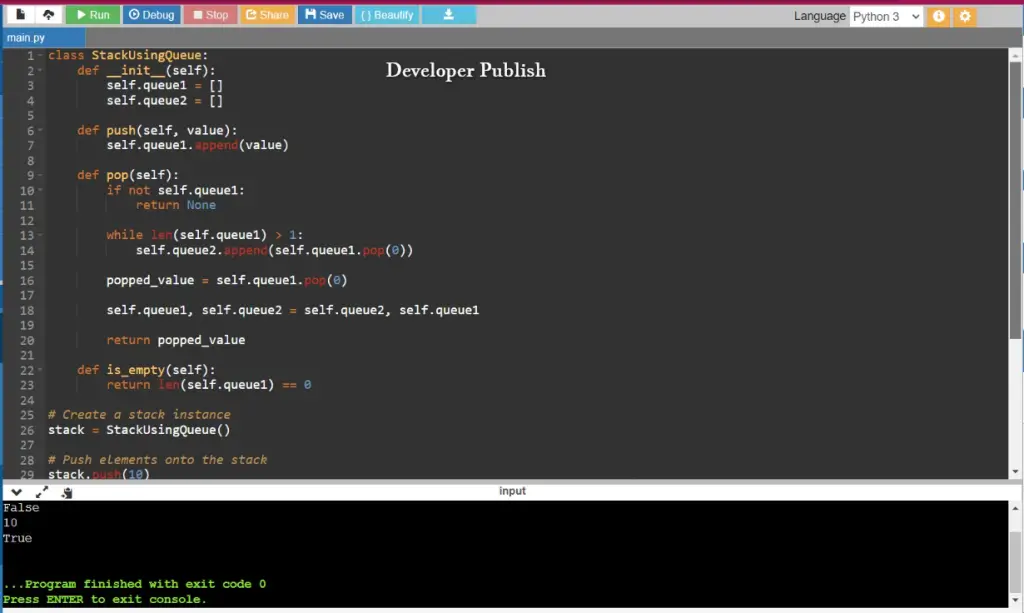
class StackUsingQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue1 = []
self.queue2 = []
def push(self, value):
self.queue1.append(value)
def pop(self):
if not self.queue1:
return None
while len(self.queue1) > 1:
self.queue2.append(self.queue1.pop(0))
popped_value = self.queue1.pop(0)
self.queue1, self.queue2 = self.queue2, self.queue1
return popped_value
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.queue1) == 0
# Create a stack instance
stack = StackUsingQueue()
# Push elements onto the stack
stack.push(10)
stack.push(20)
stack.push(30)
# Pop elements from the stack
print(stack.pop()) # Output: 30
print(stack.pop()) # Output: 20
# Check if the stack is empty
print(stack.is_empty()) # Output: False
print(stack.pop()) # Output: 10
print(stack.is_empty()) # Output: True
How It Works
- We use two queues,
queue1andqueue2, to simulate the stack behavior. - The
pushoperation is straightforward and is performed onqueue1. - The
popoperation is implemented by transferring all elements except the last one fromqueue1toqueue2. The last element is then popped fromqueue1, effectively mimicking the behavior of a stack’spopoperation. - The
is_emptymethod simply checks ifqueue1is empty.
Input/Output




Leave a Review