Python Program to Create a Class which Performs Basic Calculator Operations
This Python program defines a Calculator class with four basic calculator operations
Problem Statement
You are tasked with creating a Python class that simulates a basic calculator. The class should have methods to perform common calculator operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Python Program to Create a Class which Performs Basic Calculator Operations
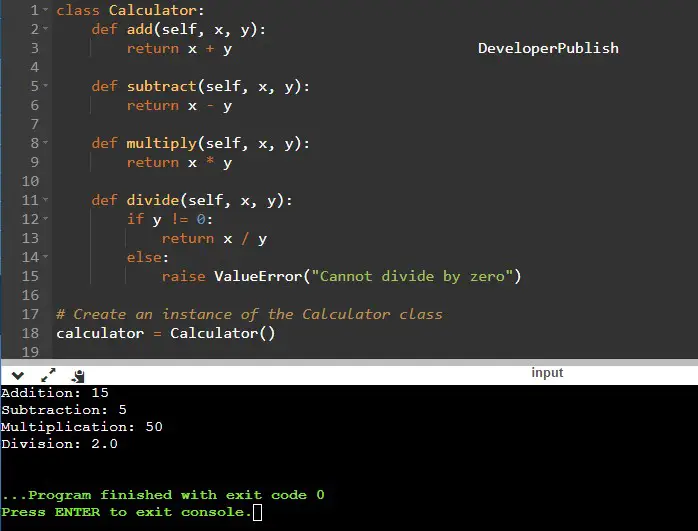
class Calculator:
def add(self, x, y):
return x + y
def subtract(self, x, y):
return x - y
def multiply(self, x, y):
return x * y
def divide(self, x, y):
if y != 0:
return x / y
else:
raise ValueError("Cannot divide by zero")
# Create an instance of the Calculator class
calculator = Calculator()
# Perform operations
print("Addition:", calculator.add(10, 5))
print("Subtraction:", calculator.subtract(10, 5))
print("Multiplication:", calculator.multiply(10, 5))
print("Division:", calculator.divide(10, 5))
How it Works
- Class Definition: The
BasicCalculatorclass is defined with four methods:add,subtract,multiply, anddivide. Each method takes two arguments (xandy) representing the numbers on which the corresponding operation should be performed. The methods are placeholders for you to implement the actual operations. - Method Implementation:
add(self, x, y): This method should calculate the sum of the two input numbersxandyand return the result.subtract(self, x, y): This method should calculate the difference between the two input numbersxandyand return the result.multiply(self, x, y): This method should calculate the product of the two input numbersxandyand return the result.divide(self, x, y): This method should calculate the division of the dividendxby the divisory. Ifyis not zero, it should return the result. However, ifyis zero, it should raise aValueErrorto indicate that division by zero is not allowed.
- Usage Example:
- You create an instance of the
BasicCalculatorclass, such ascalculator = BasicCalculator(). - You can then use the instance’s methods to perform calculator operations.
- You create an instance of the
- Output:
- The actual output will depend on the values you provide as arguments for the operations. For example, if you call
add(10, 5), the result will be15. If you calldivide(10, 0), it will raise aValueErrorwith a message indicating division by zero is not allowed.
- The actual output will depend on the values you provide as arguments for the operations. For example, if you call
Input/ Output




Leave a Review