C Program to Find Union and Intersection of Two Arrays
This C program finds the union and intersection of two arrays. It takes two arrays as input and computes the resulting union and intersection arrays.
Program Statement
Here’s the program statement for the C program to find the union and intersection of two arrays:
Program Statement:
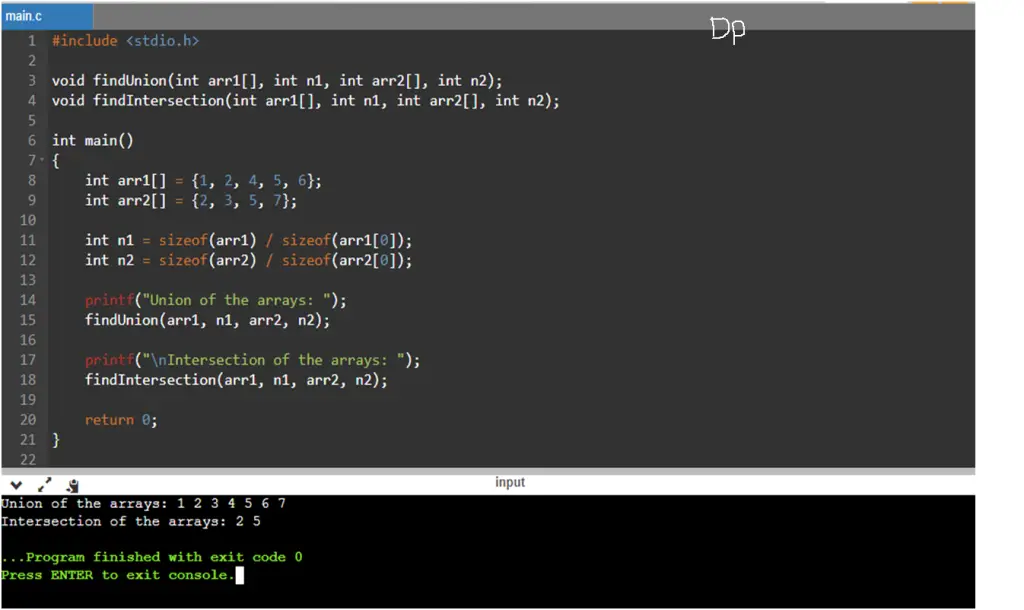
Write a C program to find the union and intersection of two arrays. The program should take two input arrays arr1 and arr2 of integers, along with their sizes n1 and n2 respectively. The program should then find and print the union of the two arrays, followed by the intersection of the two arrays.
Input:
- Two input arrays
arr1andarr2of integers. - The size of
arr1, denoted byn1. - The size of
arr2, denoted byn2.
Output:
- The union of
arr1andarr2, without any duplicates. - The intersection of
arr1andarr2, containing only the common elements.
C Program to Find Union and Intersection of Two Arrays
#include <stdio.h>
void findUnion(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
printf("%d ", arr1[i++]);
else if (arr2[j] < arr1[i])
printf("%d ", arr2[j++]);
else {
printf("%d ", arr2[j++]);
i++;
}
}
while (i < m)
printf("%d ", arr1[i++]);
while (j < n)
printf("%d ", arr2[j++]);
}
void findIntersection(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else if (arr2[j] < arr1[i])
j++;
else {
printf("%d ", arr2[j++]);
i++;
}
}
}
int main() {
int arr1[] = {1, 2, 4, 5, 6};
int arr2[] = {2, 3, 5, 7};
int m = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int n = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
printf("Union: ");
findUnion(arr1, arr2, m, n);
printf("\nIntersection: ");
findIntersection(arr1, arr2, m, n);
return 0;
}
How it works
Let me explain how the program works step by step:
- In the
mainfunction, two arraysarr1andarr2are defined, along with their respective sizesn1andn2. The example arrays are:cssCopy codearr1 = [1, 2, 4, 5, 6] arr2 = [2, 3, 5, 7] - The
findUnionfunction is called witharr1,n1,arr2, andn2as arguments. This function finds and prints the union of the two arrays. - Inside the
findUnionfunction, two variablesiandjare initialized to 0. These variables are used as indices to iterate overarr1andarr2respectively. - The function enters a loop that continues as long as
iis less thann1(the size ofarr1) andjis less thann2(the size ofarr2). - Within the loop, the function compares the elements of
arr1[i]andarr2[j]:- If
arr1[i]is less thanarr2[j], it meansarr1[i]is not present inarr2. So, the elementarr1[i]is printed as part of the union, andiis incremented to move to the next element inarr1. - If
arr2[j]is less thanarr1[i], it meansarr2[j]is not present inarr1. So, the elementarr2[j]is printed as part of the union, andjis incremented to move to the next element inarr2. - If
arr1[i]is equal toarr2[j], it means the element is common to both arrays. So, the element is printed as part of the union, and bothiandjare incremented to move to the next elements in both arrays.
- If
- After the loop ends, there may be some remaining elements in either
arr1orarr2. The function uses two separate while loops to print any remaining elements inarr1andarr2, if any. - The
findIntersectionfunction is called with the same arguments as thefindUnionfunction. This function finds and prints the intersection of the two arrays. - Inside the
findIntersectionfunction, a similar comparison loop is used to iterate overarr1andarr2. However, instead of printing elements, the function only incrementsiandjwhen the elements are not equal. When the elements are equal, it means the element is common to both arrays, so it is printed as part of the intersection. - Finally, the
mainfunction prints the output by calling theprintffunction. The union is printed first by callingfindUnion, followed by the intersection, which is printed by callingfindIntersection.
That’s how the program works! It compares the elements of the two arrays and determines the union and intersection based on the comparison results.
Input/Output

Leave a Review