Saving Files in Excel VBA
In this post, you will be learning about Saving Files in Excel VBA and the different options associated with it.
Saving Files in Excel VBA
You can save a file in Excel VBA using two different methods,
- Save
- Save as
Read along to know more about each option.
How to Run a Code in Visual Basic Editor?
As you know, to run the VBA code in Excel,
- Open the Visual Basic Editor (Alt + F11),
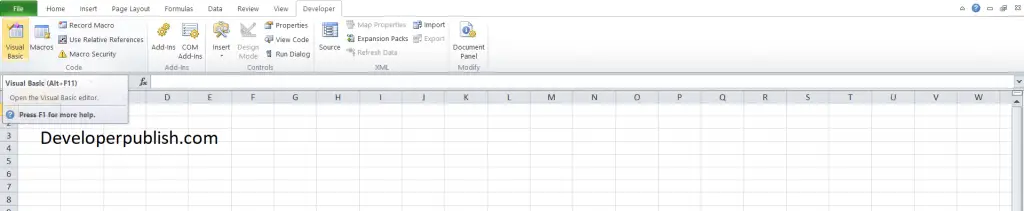
- Click on Insert a new module.
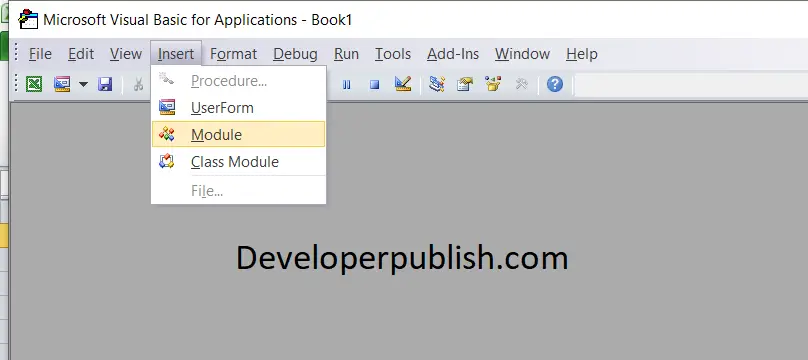
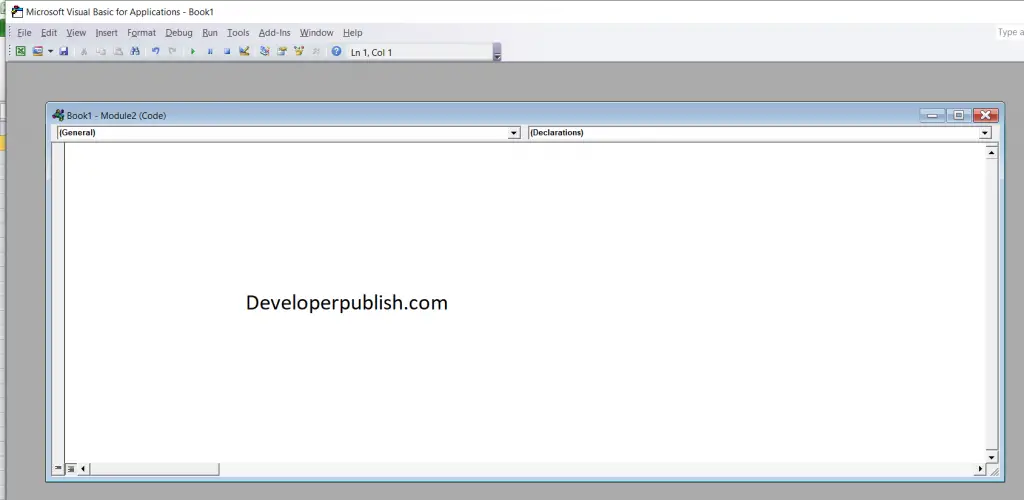
- Enter the code, save it and run it.
Save Workbook or a File using Save option
Let’s see the different ways of saving a workbook using Excel VBA using the save workbook option.
Save Active Workbook
To save an active workbook in Excel VBA, enter the following code in the module and click run.
Code
Sub VBA_SaveWorkBook() ActiveWorkbook.Save End Sub
Save Specific Workbook
If you want to save a specific workbook, you need to specify the name of the workbook in the below code and run it.
Code
Sub ActivateWorkbook()
Workbooks("name.xlsx").Activate
End SubSave All Open Workbooks
To save the all open workbook in Excel VBA, enter the following code in the module and click run.
Code
Dim wb as workbook
For Each wb In Application.Workbooks
wb.Save
Next wbSave the workbook using Index
To save workbook using index in Excel VBA, enter the following code in the module and click run.
This code consists of a loop, hence while running this code, it saves all the other workbooks other than the one with this code.
Code
Sub CloseWorkbooks() Dim WbCount As Integer WbCount = Workbooks.Count For i = WbCount To 1 Step -1 If Workbooks(i).Name <> ThisWorkbook.Name Then Workbooks(i).Close End If Next i End Sub
Save As in Excel VBA
The Save As command saves an Excel file as a new file, similar to clicking the Save As icon. Save As works similarly to the Save option, except you need to specify the name of the new file.
Syntax for Save As command
workbook object .SaveAs(FileName, FileFormat, Password, WriteResPassword, _
ReadOnlyRecommended, CreateBackup, AccessMode, ConflictResolution, _
AddToMru,TextCodepage, TextVisualLayout, Local)
The bellow are the different ‘save as’ options available.
Workbook Save As – Same Directory
To save a file in the same directory using save as option,
Code
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "new"
or
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs "new"
or
Dim wbstring as string wbstring = "new" ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstring
Workbook Save As – New Directory
Code
To save a file in a new directory using save as option,
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:\new"
or
Dim wbstring as string wbstring = "C:\new" ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstring
Workbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension
To save a file in the new directory with a specified file extension using save as option,
Code
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:\new.xlsx"
or
Dim wbstring as string wbstring = "C:\new.xlsx" ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstring
Workbook Save As – Add Password to Open File
To save a file and add password to open the file
Code
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:\new.xlsx", Password:= "password"
- Workbook Save As – Add Password for Write Privileges
Incase of incorrect password, then the workbook opens in Read-Only format.
Code
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:\new.xlsx", WriteRes:= "password"


Leave a Review