Python Program to Implement Queue
In this Python program, we will implement a queue data structure using a list. A queue follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle, where the element added first is the one that will be removed first.
Problem Statement
Implement a queue data structure using a list and provide methods to enqueue (add) elements to the rear and dequeue (remove) elements from the front of the queue.
Python Program to Implement Queue
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
def enqueue(self, item):
self.queue.append(item)
def dequeue(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.queue.pop(0)
else:
return "Queue is empty"
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.queue) == 0
def size(self):
return len(self.queue)
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
q = Queue()
q.enqueue(10)
q.enqueue(20)
q.enqueue(30)
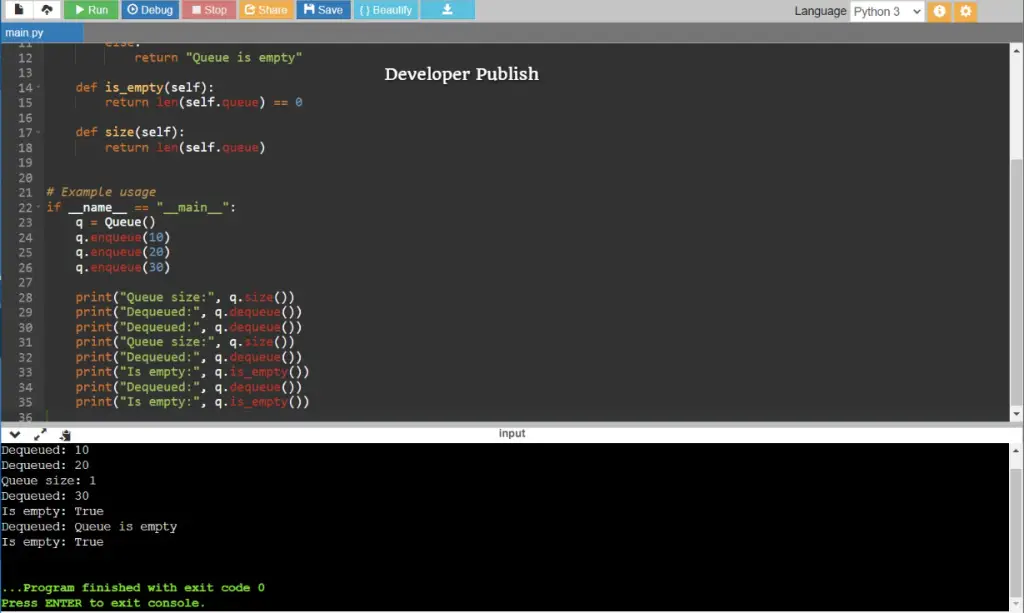
print("Queue size:", q.size())
print("Dequeued:", q.dequeue())
print("Dequeued:", q.dequeue())
print("Queue size:", q.size())
print("Dequeued:", q.dequeue())
print("Is empty:", q.is_empty())
print("Dequeued:", q.dequeue())
print("Is empty:", q.is_empty())
How It Works
- The
Queueclass is defined with methods to perform queue operations. - The
enqueuemethod appends the given item to the end of the queue. - The
dequeuemethod removes and returns the first item from the front of the queue. - The
is_emptymethod checks if the queue is empty. - The
sizemethod returns the current size of the queue.
Input/Output




Leave a Review