Python Program Find the Length of Linked List using Recursion
In this Python program, we will use recursion to find the length of a linked list. A linked list is a data structure consisting of nodes where each node contains data and a reference (or pointer) to the next node in the sequence.
Problem statement
Given a linked list, we need to calculate the length of the linked list using recursion.
Python Program Find the Length of Linked List using Recursion
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def length_recursive(self, node):
if node is None:
return 0
return 1 + self.length_recursive(node.next)
def get_length(self):
return self.length_recursive(self.head)
llist = LinkedList()
llist.append(10)
llist.append(20)
llist.append(30)
llist.append(40)
print("Length of the linked list:", llist.get_length())
How it works
- We define a
Nodeclass to represent individual nodes of the linked list. Each node contains data and a reference to the next node. - We define a
LinkedListclass with methods to append nodes and find the length of the linked list. - The
length_recursivemethod takes a node as an argument and recursively calculates the length of the linked list starting from that node. - In the
get_lengthmethod, we initiate the recursive length calculation from the head node of the linked list. - We create a linked list using the
LinkedListclass and append some nodes to it. - Finally, we call the
get_lengthmethod to calculate and print the length of the linked list.
Input / Output
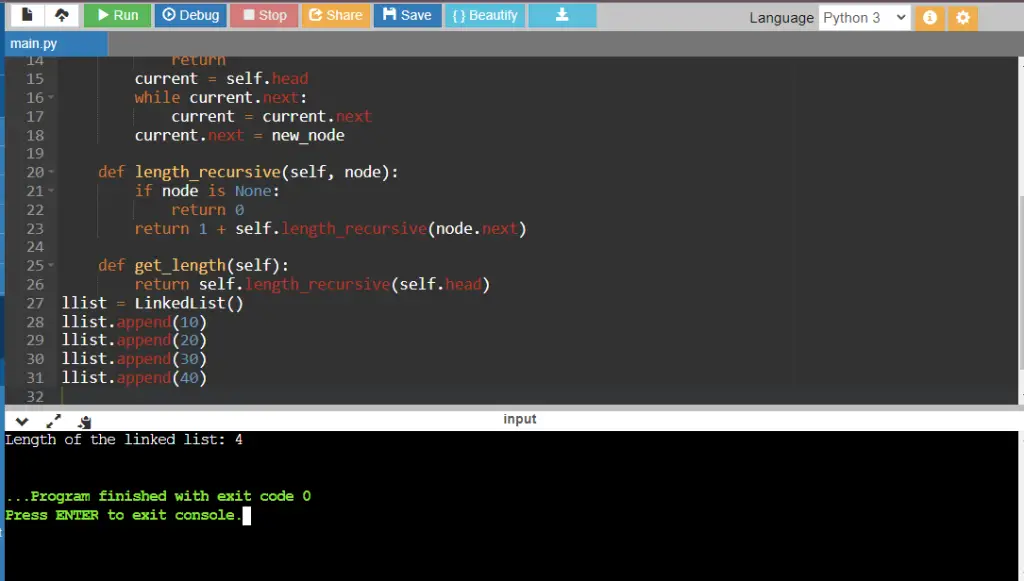




Leave a Review