C Program to Print the Program Name and All its Arguments
This C program prints the name of the program and all its command-line arguments.
In C programming, command-line arguments allow us to pass inputs to a program when it is executed. These arguments can provide additional information or parameters to control the behavior of the program. In this context, we will develop a C program that prints the program name and all the arguments passed to it.
Problem statement
Write a C program that accepts command-line arguments and prints the program name followed by each argument, along with their respective indices.
C Program to Print the Program Name and All its Arguments
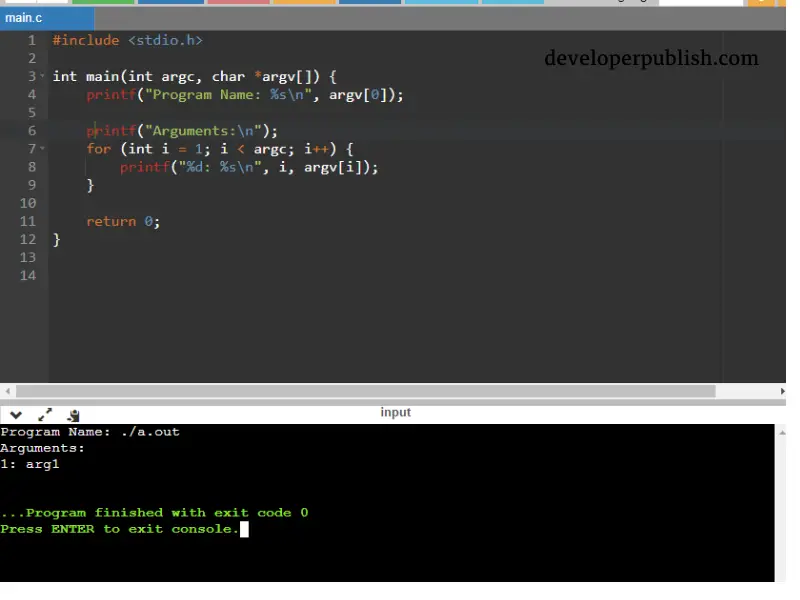
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
printf("Program Name: %s\n", argv[0]);
printf("Arguments:\n");
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
printf("%d: %s\n", i, argv[i]);
}
return 0;
}
How it works
- The program starts by including the necessary header file
stdio.hfor input and output operations. - The
mainfunction is the entry point of the program and accepts two parameters:argcandargv.argcrepresents the number of command-line arguments, whileargvis an array of strings containing those arguments. - The program uses the
printffunction to display the program name (argv[0]) using the format specifier%s. - It then prints the header “Arguments:” to indicate the list of command-line arguments.
- A
forloop is used to iterate over the command-line arguments starting from index 1 (sinceargv[0]contains the program name). - Within the loop, the program uses
printfto display the index of each argument (i) along with the argument itself (argv[i]). - Finally, the
return 0;statement signifies the successful execution of the program.
Input/output

Leave a Review