C Program to Find Mean, Variance and Standard Deviation
This C program calculates the mean, variance, and standard deviation of a set of numbers. These statistical measures are commonly used in data analysis and statistics to describe the central tendency, spread, and dispersion of a dataset.
Problem statement
Write a C program that takes a set of numbers as input and calculates the mean, variance, and standard deviation of the given set.
C Program to Find Mean, Variance and Standard Deviation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main() {
int n, i;
float sum = 0.0, mean, variance = 0.0, stdDeviation;
printf("Enter the number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
float numbers[n];
printf("Enter %d elements:\n", n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%f", &numbers[i]);
sum += numbers[i];
}
mean = sum / n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
variance += pow(numbers[i] - mean, 2);
}
variance /= n;
stdDeviation = sqrt(variance);
printf("Mean: %.2f\n", mean);
printf("Variance: %.2f\n", variance);
printf("Standard Deviation: %.2f\n", stdDeviation);
return 0;
}
How It Works
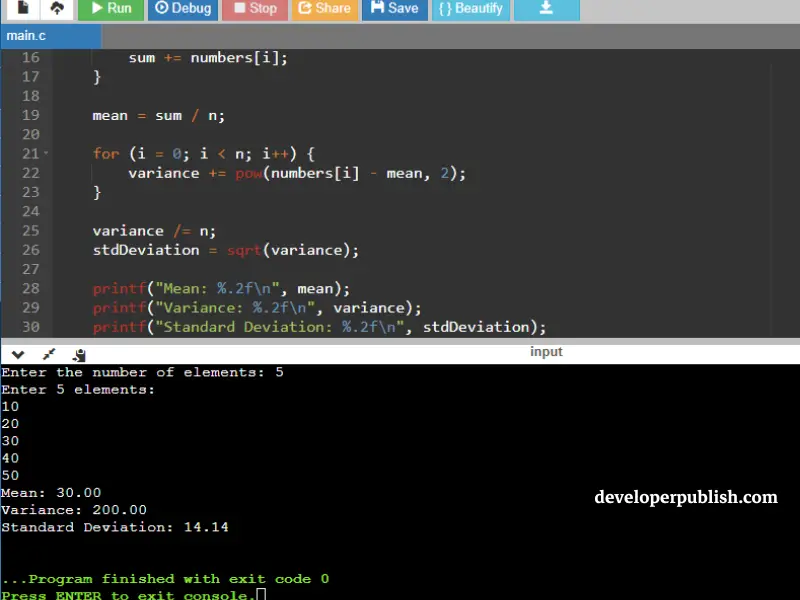
- The user is prompted to enter the number of elements, in this case, 5.
- The program then asks the user to input each element of the dataset.
- The sum of all the elements is calculated to find the mean.
- The variance is calculated by subtracting the mean from each element, squaring the result, and summing up the squares.
- The variance is divided by the number of elements to get the average variance.
- The standard deviation is calculated as the square root of the variance.
- The program finally displays the calculated mean, variance, and standard deviation.
Input\output

Leave a Review