C Program to Find HCF of Two Numbers
This C program finds the Highest Common Factor (HCF) of two given numbers using recursion.
Problem Statement
Write a C program that finds the Highest Common Factor (HCF) of two numbers using the Euclidean algorithm.
Input: The user is prompted to enter two integers, num1 and num2, representing the two numbers for which the HCF needs to be calculated.
Output: The program calculates the HCF using the Euclidean algorithm and prints the result, which is the HCF of the two input numbers.
Note:
The Euclidean algorithm is an efficient method for finding the HCF of two numbers. It repeatedly divides the larger number by the smaller number and updates the values until the remainder becomes zero. The HCF is the value of the last non-zero remainder obtained during this process.
C Program to Find HCF of Two Numbers
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate HCF using the Euclidean algorithm
int calculateHCF(int num1, int num2) {
int remainder;
// Make sure num1 is always greater than or equal to num2
if (num2 > num1) {
int temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
}
// Calculate HCF using the Euclidean algorithm
while (num2 != 0) {
remainder = num1 % num2;
num1 = num2;
num2 = remainder;
}
return num1; // num1 holds the HCF
}
int main() {
int num1, num2;
printf("Enter the first number: ");
scanf("%d", &num1);
printf("Enter the second number: ");
scanf("%d", &num2);
// Call the calculateHCF function and store the result
int hcf = calculateHCF(num1, num2);
printf("The HCF of %d and %d is %d.\n", num1, num2, hcf);
return 0;
}
How it Works
- The program starts by including the necessary header file
stdio.hfor input/output operations. - The program defines a function
calculateHCFthat takes two integer argumentsnum1andnum2and returns the HCF. - Inside the
calculateHCFfunction, a variableremainderis declared to store the remainder of the division operation. - To simplify the calculation, the program checks if
num2is greater thannum1. If so, it swaps the values ofnum1andnum2using a temporary variabletemp. This ensures thatnum1is always greater than or equal tonum2. - The Euclidean algorithm is then applied iteratively. It divides
num1bynum2and assigns the remainder toremainder. It updatesnum1with the value ofnum2andnum2with the value ofremainder. - The algorithm continues this process until
num2becomes zero. At this point,num1holds the HCF, which is returned by thecalculateHCFfunction. - The program then defines the
mainfunction, which is the entry point of the program. - Inside the
mainfunction, two integer variablesnum1andnum2are declared to store the user-input numbers. - The program prompts the user to enter the first number using the
printffunction and reads the input using thescanffunction. - Similarly, the program prompts the user to enter the second number and reads the input.
- The
calculateHCFfunction is called with the user-provided numbersnum1andnum2, and the returned HCF value is stored in the variablehcf. - Finally, the program uses the
printffunction to display the calculated HCF along with the input numbers. - The program ends by returning 0, indicating successful execution.
When you run the program, it prompts you to enter two numbers. It then calculates their HCF using the Euclidean algorithm and displays the result on the console.
Input /Output
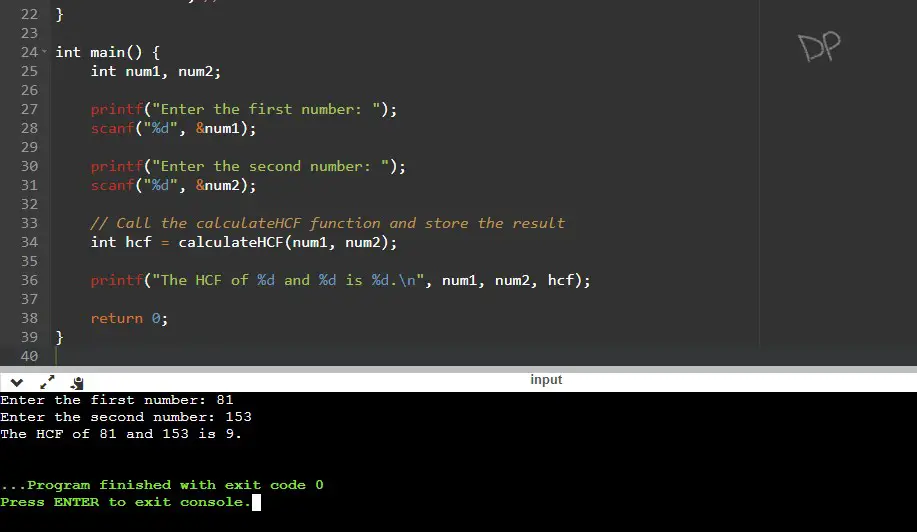
In this case, the user inputs the numbers 81 and 153. The program calculates their HCF using the Euclidean algorithm, which gives a result of 9.

Leave a Review