Python Program to Read a Linked List in Reverse
This Python program demonstrates how to read a singly linked list in reverse order using a recursive approach.
Problem Statement
You are given the task of implementing a program to read and print a linked list in reverse order. A linked list is a data structure consisting of nodes, where each node contains data and a reference to the next node in the list.
Python Program to Read a Linked List in Reverse
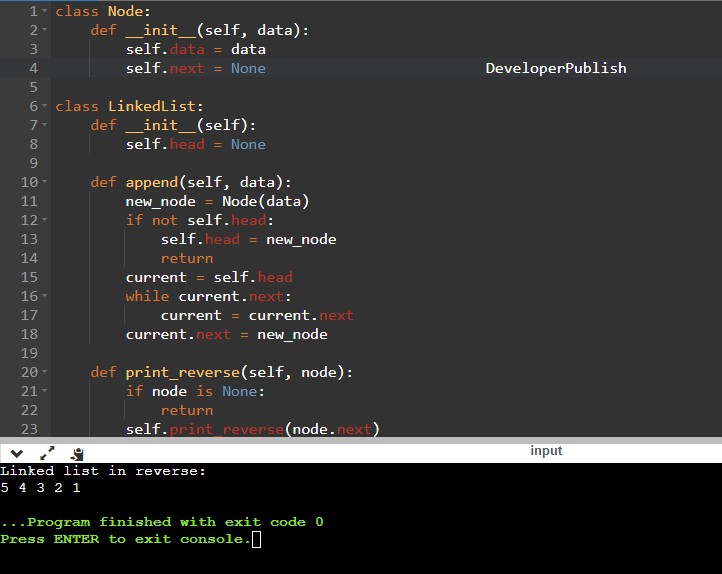
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def print_reverse(self, node):
if node is None:
return
self.print_reverse(node.next)
print(node.data, end=" ")
def reverse_print(self):
self.print_reverse(self.head)
# Creating a linked list
llist = LinkedList()
llist.append(1)
llist.append(2)
llist.append(3)
llist.append(4)
llist.append(5)
print("Linked list in reverse:")
llist.reverse_print()
How it Works
- Defining the Node Class:
- The
Nodeclass defines a blueprint for creating nodes in the linked list. - Each node has two attributes:
datato store the value of the node, andnextto store a reference to the next node in the list. Initially,nextis set toNone.
- The
- Defining the LinkedList Class:
- The
LinkedListclass manages the linked list as a whole. - It has an
__init__constructor method that initializes the linked list. It sets the initial value of theheadattribute toNone.
- The
- Appending Nodes to the Linked List:
- The
appendmethod in theLinkedListclass is used to add nodes to the end of the linked list. - If the linked list is empty (i.e.,
headisNone), the new node becomes the head. - Otherwise, it traverses the linked list to find the last node and then adds the new node after it.
- The
- Printing in Reverse using Recursion:
- The
print_reversemethod is used to print the linked list in reverse order using a recursive approach. - It takes a node as an argument.
- Inside the method, it first checks if the given node is
None. If it is, the recursion stops. - Otherwise, it recursively calls itself with the next node in the list. This continues until it reaches the last node.
- During the recursive unwinding (when the recursion starts to backtrack), it prints the data of each node. Because of the recursive nature, this effectively prints the linked list in reverse order.
- The
- Wrapper for Reverse Printing:
- The
reverse_printmethod serves as a wrapper to initiate the recursive printing of the linked list in reverse. - It calls the
print_reversemethod with the initialheadnode of the linked list.
- The
- Creating and Using the Linked List:
- An instance of the
LinkedListclass, namedllist, is created. - Nodes with values 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 are appended to the linked list using the
appendmethod.
- An instance of the
- Printing the Linked List in Reverse:
- The program calls the
reverse_printmethod on thellistobject. - This starts the recursive process of printing the linked list in reverse order.
- The program calls the
- Output:
- The program outputs the linked list elements in reverse order: “5 4 3 2 1”.
Input/ Output




Leave a Review