Python Program to Implement Depth First Search Traversal using Post Order
This Python program explores Depth-First Search (DFS) traversal in a binary tree, specifically using the post-order technique. Post-order traversal follows the sequence: left subtree, right subtree, and then the root. This program demonstrates essential tree traversal methods and the practical use of post-order traversal in binary trees.
Problem Statement
The goal is to write a Python program that performs a depth-first search (DFS) traversal of a binary tree using the post-order technique. Post-order traversal is particularly useful for tasks such as deleting nodes or evaluating expressions within the tree.
Python Program to Implement Depth First Search Traversal using Post Order
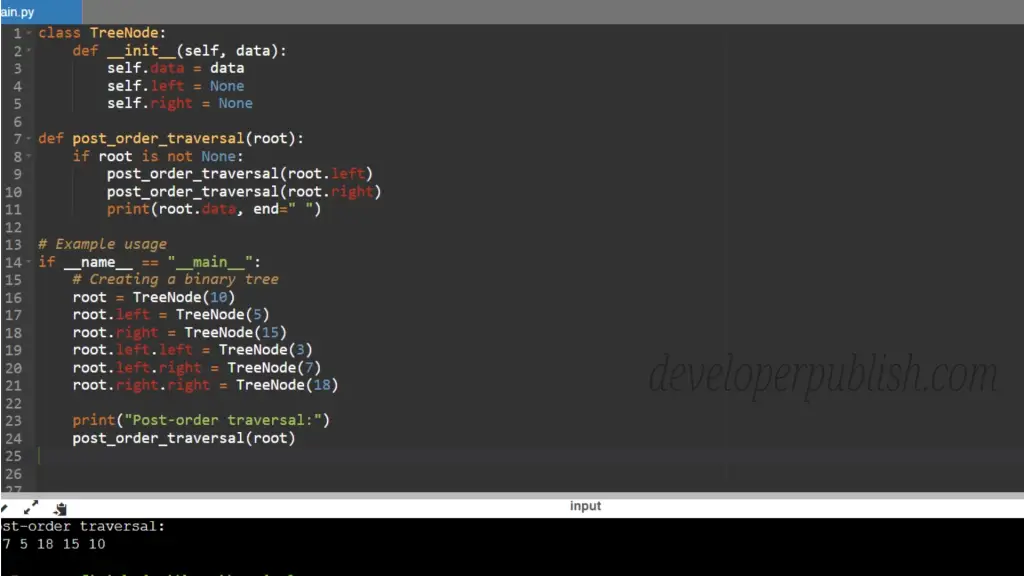
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def post_order_traversal(root):
if root is not None:
post_order_traversal(root.left)
post_order_traversal(root.right)
print(root.data, end=" ")
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Creating a binary tree
root = TreeNode(10)
root.left = TreeNode(5)
root.right = TreeNode(15)
root.left.left = TreeNode(3)
root.left.right = TreeNode(7)
root.right.right = TreeNode(18)
print("Post-order traversal:")
post_order_traversal(root)
Input / Output




Leave a Review