Python Program to Find All Reachable Nodes in a Graph using BFS
In this Python program, we will use Breadth-First Search (BFS) to find all reachable nodes in a graph starting from a given source node. BFS is a widely used graph traversal algorithm that explores all the neighbors of a node before moving to their children, making it perfect for finding reachable nodes from a starting point.
Problem Statement
Given a graph represented as an adjacency list and a source node, we need to find all the nodes that are reachable from the source node using BFS.
Python Program to Find All Reachable Nodes in a Graph using BFS
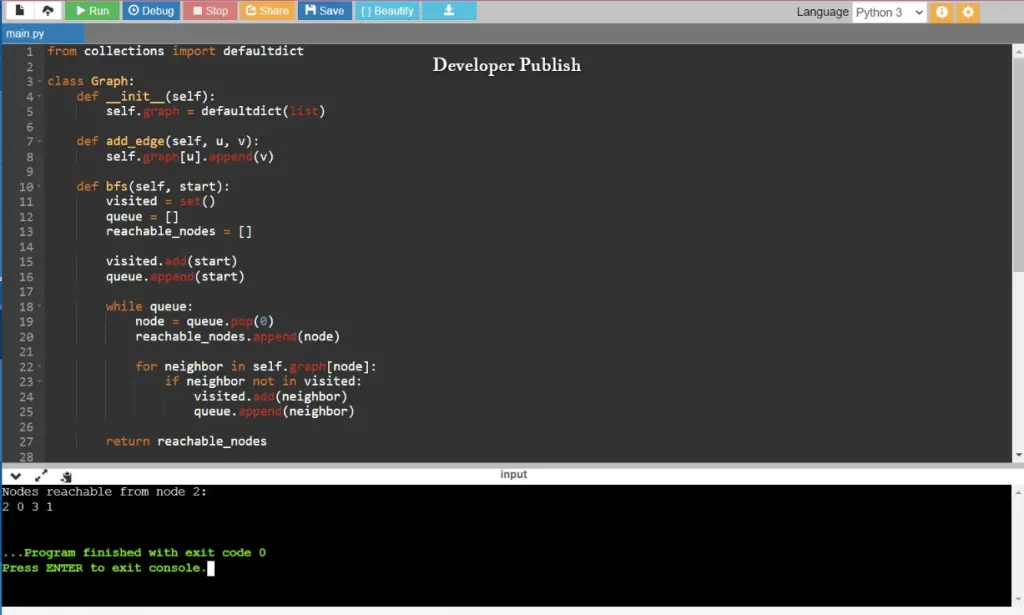
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
def add_edge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
def bfs(self, start):
visited = set()
queue = []
reachable_nodes = []
visited.add(start)
queue.append(start)
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
reachable_nodes.append(node)
for neighbor in self.graph[node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
visited.add(neighbor)
queue.append(neighbor)
return reachable_nodes
def main():
graph = Graph()
# Add edges to the graph (example)
graph.add_edge(0, 1)
graph.add_edge(0, 2)
graph.add_edge(1, 2)
graph.add_edge(2, 0)
graph.add_edge(2, 3)
graph.add_edge(3, 3)
source_node = 2 # Change this to your desired source node
reachable_nodes = graph.bfs(source_node)
print(f"Nodes reachable from node {source_node}:")
for node in reachable_nodes:
print(node, end=" ")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
How it Works
- We define a
Graphclass to represent the graph using an adjacency list. - The
add_edgemethod is used to add edges to the graph. - The
bfsmethod performs a BFS traversal starting from the given source node. It uses a queue to keep track of nodes to be visited. - We maintain a
visitedset to ensure that we don’t visit a node multiple times. - The reachable nodes are stored in the
reachable_nodeslist and returned as the result.
Input/Output




Leave a Review