Python Program to Count Non Leaf Nodes in a Tree
This Python program counts the number of non-leaf nodes in a given tree data structure. A tree is a hierarchical structure where each node can have zero or more child nodes, and non-leaf nodes are those that have at least one child.
Problem Statement
Given a tree, the program aims to count the number of non-leaf nodes present in the tree.
Python Program to Count Non Leaf Nodes in a Tree
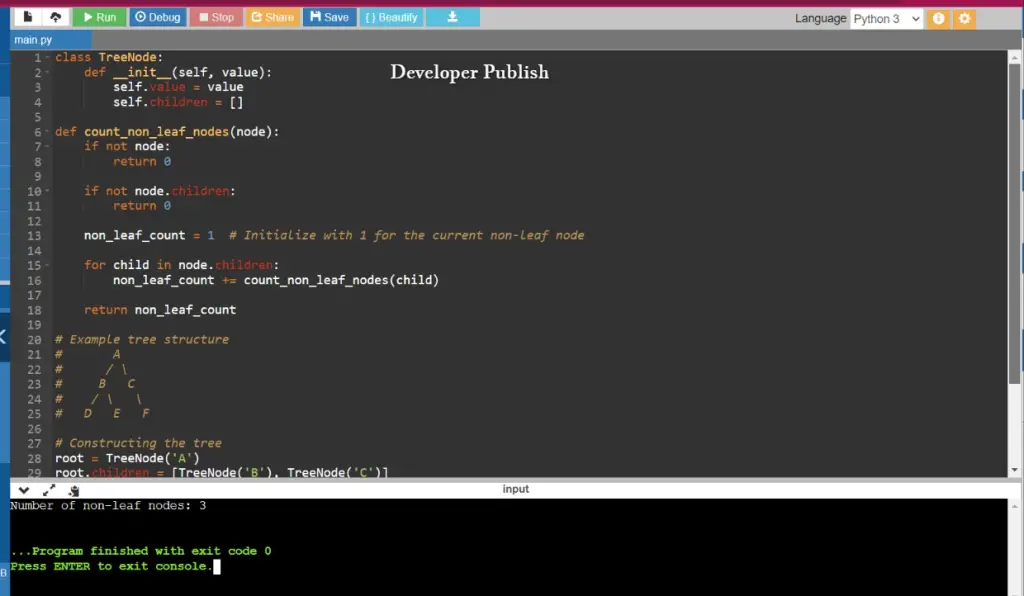
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.children = []
def count_non_leaf_nodes(node):
if not node:
return 0
if not node.children:
return 0
non_leaf_count = 1 # Initialize with 1 for the current non-leaf node
for child in node.children:
non_leaf_count += count_non_leaf_nodes(child)
return non_leaf_count
# Example tree structure
# A
# / \
# B C
# / \ \
# D E F
# Constructing the tree
root = TreeNode('A')
root.children = [TreeNode('B'), TreeNode('C')]
root.children[0].children = [TreeNode('D'), TreeNode('E')]
root.children[1].children = [TreeNode('F')]
# Count non-leaf nodes
result = count_non_leaf_nodes(root)
print("Number of non-leaf nodes:", result)
How It Works
The program defines a TreeNode class representing a node in the tree. Each node contains a value and a list of children nodes. The count_non_leaf_nodes function recursively traverses the tree and counts the non-leaf nodes. If a node has no children, it’s not considered a non-leaf node. Otherwise, the function traverses each child node and accumulates the count. The count starts at 1 for the current non-leaf node.
Input/Output




Leave a Review