Python Program to Add Corresponding Positioned Elements of Two Linked Lists
In this python program, we’re addressing the task of adding corresponding positioned elements of two linked lists. Linked lists are widely used data structures, and this program demonstrates how to perform element-wise addition between two linked lists.
Problem Statement
Given two linked lists with the same length, your goal is to create a new linked list where each node’s value is the sum of the values at the corresponding positions in the input linked lists.
Python Program to Add Corresponding Positioned Elements of Two Linked Lists
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
else:
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" -> ")
current = current.next
print("None")
def add_linked_lists(list1, list2):
result = LinkedList()
current1 = list1.head
current2 = list2.head
while current1 and current2:
total = current1.data + current2.data
result.append(total)
current1 = current1.next
current2 = current2.next
return result
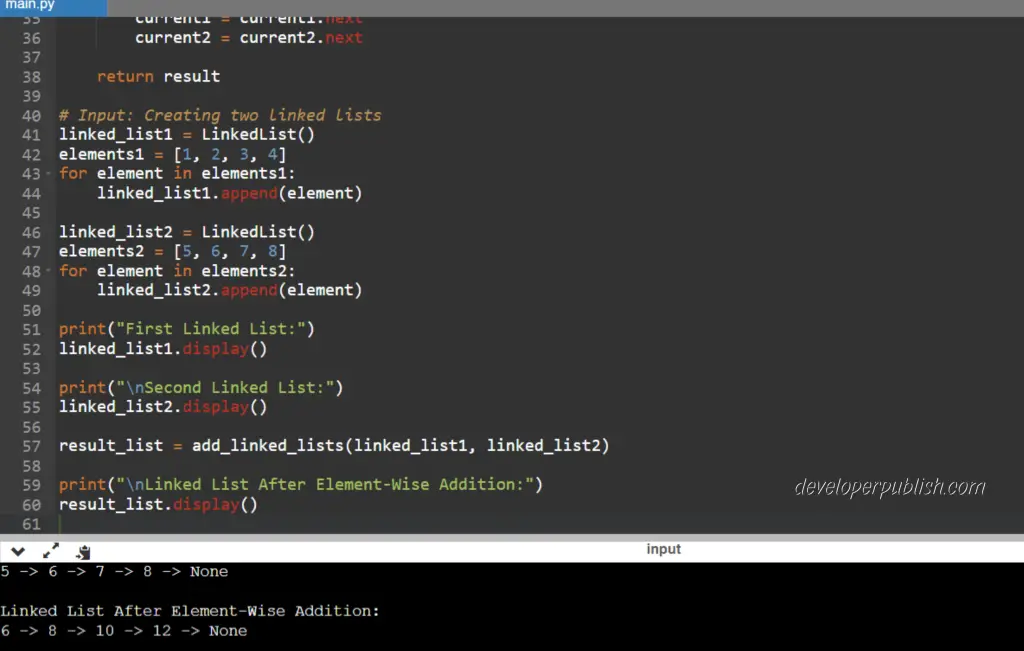
# Input: Creating two linked lists
linked_list1 = LinkedList()
elements1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
for element in elements1:
linked_list1.append(element)
linked_list2 = LinkedList()
elements2 = [5, 6, 7, 8]
for element in elements2:
linked_list2.append(element)
print("First Linked List:")
linked_list1.display()
print("\nSecond Linked List:")
linked_list2.display()
result_list = add_linked_lists(linked_list1, linked_list2)
print("\nLinked List After Element-Wise Addition:")
result_list.display()
Input / Output




Leave a Review