PERMUT Function in Excel
In this article, you will learn about the PERMUT function, the formula syntax and usage of the function in Microsoft Excel.
PERMUT Function in Excel
The PERMUT function in Excel returns the number of permutations for a given number of items/objects. Generally, permutation is any set or subset of objects or events where the internal order or the number of possibilities is significant.
The PERMUT function does not allow repetitions.
It is commonly used for lottery-style probability calculations.
Syntax
= PERMUT(number, number_chosen)
Arguments:
- Number – An integer that describes the number of objects.
- Number_chosen – An integer that describes the number of objects in each permutation.
Usage Notes and Possible Errors
- Both arguments are truncated to integers.
- When any one of the argument is nonnumeric, the PERMUT function returns the #VALUE! error value.
- When the argument, number ≤ 0 or if number_chosen < 0, the PERMUT function returns the #NUM! error value.
- The PERMUT function returns the #NUM! error value, when the number is greater than number_chosen.
- The equation or the mathematical formula for the number of permutations is:

How to use the PERMUT function in Excel?
Using this function in a WS is simple; all you need to do is enter the function as a formula of the cell in the formula bar.
Take a look at the given example
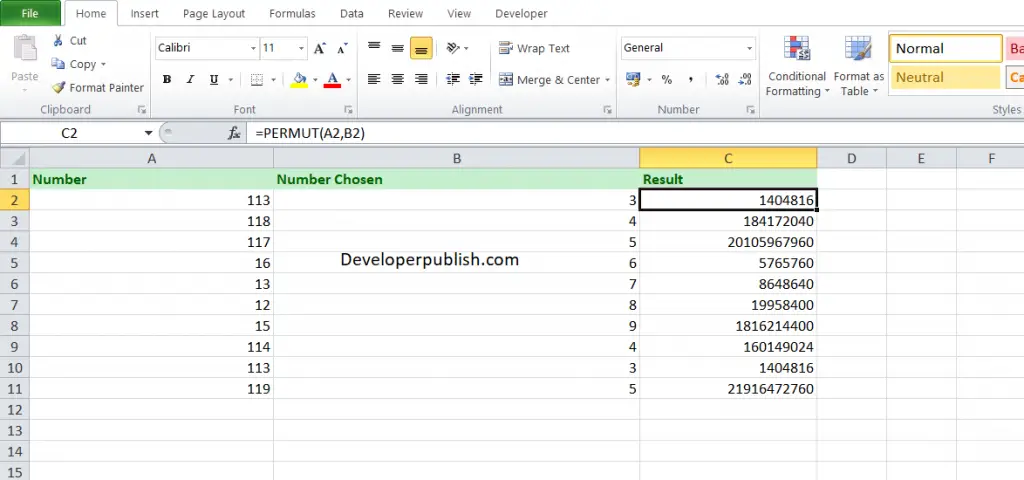
Enter the data in the respective columns and enter the PERMUT function formula.
Formula: = PERMUT(A2,B2)
Here, A2 refers to the cell name or the cell address. Column A denotes the number and Column B denotes the number of objects in each permutation.
You will get the result in the Result column.


Leave a Review