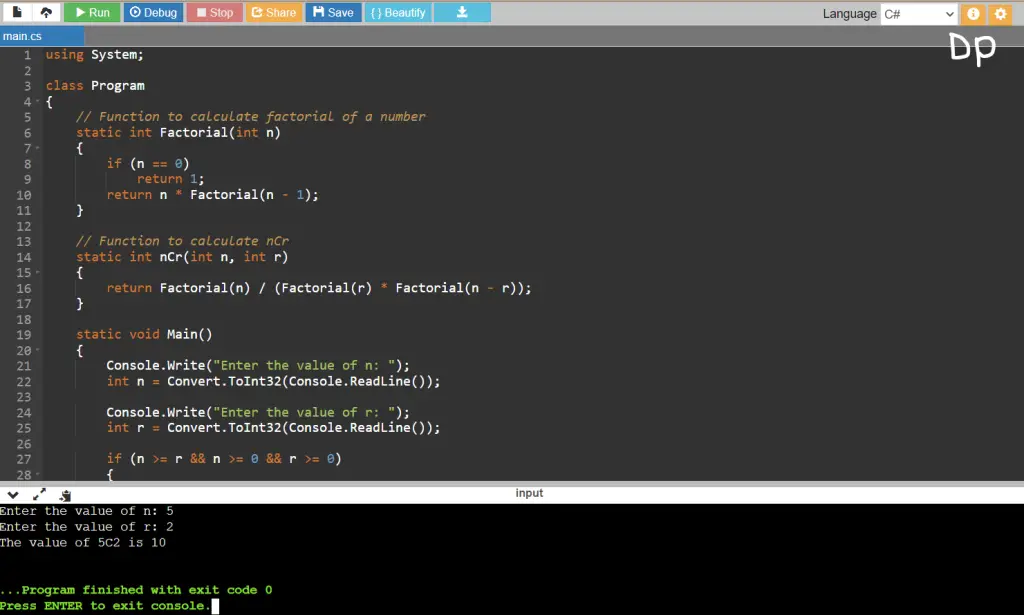
C# Program to Find nCr
This C# program calculates the combination value C(n, r), often referred to as “n choose r” or “nCr.” In combinatorial mathematics, C(n, r) represents the number of ways to choose r items from a set of n distinct items without regard to the order of selection. It is computed using the formula C(n, r) = n! / (r! * (n – r)!), where “!” denotes the factorial of a number.
Problem statement
Write a C# program that calculates the combination (nCr) of two non-negative integers, n and r.
C# Program to Find nCr
using System;
class Program
{
// Function to calculate factorial of a number
static int Factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
return n * Factorial(n - 1);
}
// Function to calculate nCr
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return Factorial(n) / (Factorial(r) * Factorial(n - r));
}
static void Main()
{
Console.Write("Enter the value of n: ");
int n = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter the value of r: ");
int r = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (n >= r && n >= 0 && r >= 0)
{
int result = nCr(n, r);
Console.WriteLine($"The value of {n}C{r} is {result}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid input. Make sure n >= r and both are non-negative.");
}
}
}
How it works
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the program works:
Factorial Function:
Code:
static int Factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
return n * Factorial(n – 1);
}
- This function calculates the factorial of a given number
n. - It’s a recursive function. When
nis 0, it returns 1 (since0! = 1). - Otherwise, it recursively multiplies
nwith the factorial of(n-1)untilnbecomes 0.
nCr Function:
Code:
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return Factorial(n) / (Factorial(r) * Factorial(n – r));
}
- This function uses the
Factorialfunction to calculate the combination (nCr). - It applies the combination formula:
nCr = n! / (r! * (n - r)!).
User Input:
Code:
static void Main()
{
Console.Write("Enter the value of n: ");
int n = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter the value of r: ");
int r = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
The Main method prompts the user to enter values for n and r using Console.ReadLine() and converts them to integers.
Input Validation:
Code:
if (n >= r && n >= 0 && r >= 0)
{
// Calculate nCr
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(“Invalid input. Make sure n >= r and both are non-negative.”);
}
It checks if the input is valid. n must be greater than or equal to r and both must be non-negative.
Calculate nCr:
Code:
int result = nCr(n, r);
Console.WriteLine($”The value of {n}C{r} is {result}”);
- If the input is valid, it calculates the value of nCr using the
nCrfunction and prints the result.
Output:
That’s how the program works! It takes user input for n and r, validates the input, calculates nCr if the input is valid, and displays the result. If the input is invalid, it provides an appropriate error message.
Input/Output


Leave a Review