SQL Server Error Msg 158 – An aggregate may not appear in the OUTPUT clause
In this blog post, let’s learn about the error message “158 – An aggregate may not appear in the OUTPUT clause.” in Microsoft SQL Server, the reason why it appears and the solution to fix it.
SQL Server Error Message
158 – An aggregate may not appear in the OUTPUT clause
Reason for the Error
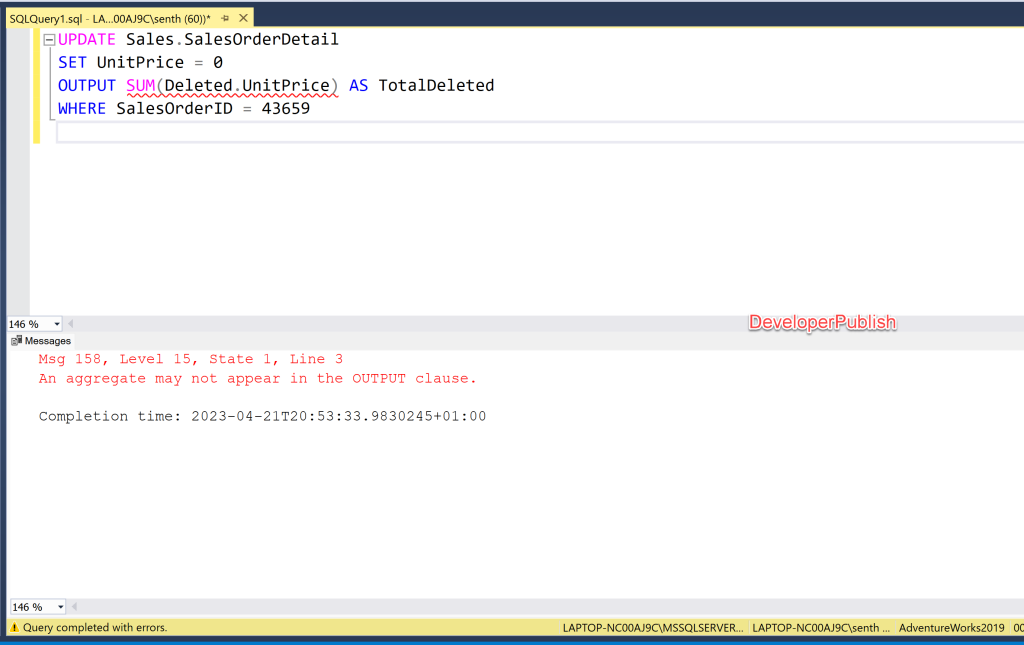
Here’s an example using the AdventureWorks2019 database that demonstrates the SQL Server Error Msg “An aggregate may not appear in the OUTPUT clause”:
UPDATE Sales.SalesOrderDetail SET UnitPrice = 0 OUTPUT SUM(Deleted.UnitPrice) AS TotalDeleted WHERE SalesOrderID = 43659
This UPDATE statement attempts to update the UnitPrice column in the Sales.SalesOrderDetail table and also output the sum of the deleted UnitPrice values using the SUM function in the OUTPUT clause. However, this is not allowed because aggregate functions are designed to operate on sets of rows, not individual rows.
Solution
To correct this error, you should remove the aggregate function from the OUTPUT clause or modify the statement to only return scalar values. Here’s an example of how you could modify the previous statement:
DECLARE @TotalDeleted MONEY UPDATE Sales.SalesOrderDetail SET UnitPrice = 0 OUTPUT SUM(Deleted.UnitPrice) AS TotalDeleted INTO @TotalDeleted WHERE SalesOrderID = 43659
In this example, the aggregate function SUM is used in the OUTPUT clause to calculate the total of the deleted UnitPrice values, which is then stored in the @TotalDeleted variable. This modification allows the statement to output a scalar value (a single sum) into the @TotalDeleted variable without using an aggregate function.


Leave a Review