Python Program to Perform Binary Search using Recursion
This Python program demonstrates the implementation of binary search using recursion. Binary search is an efficient algorithm to find a specific element in a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half.
Problem Statement
Write a Python program that performs a binary search on a sorted array using recursion to find a target element. The program should return the index of the target element if found, otherwise return -1.
Python Program to Perform Binary Search using Recursion
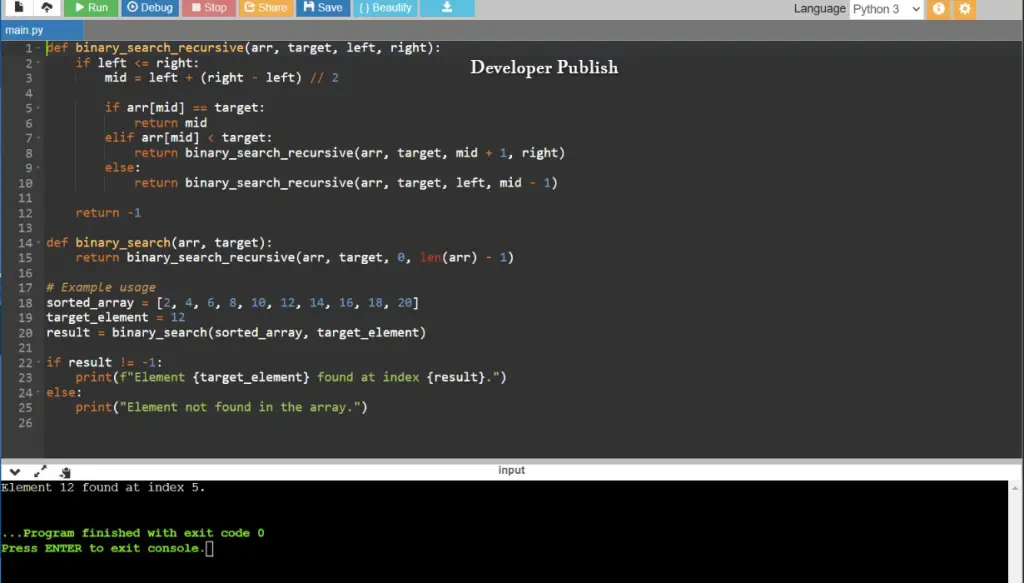
def binary_search_recursive(arr, target, left, right):
if left <= right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
return binary_search_recursive(arr, target, mid + 1, right)
else:
return binary_search_recursive(arr, target, left, mid - 1)
return -1
def binary_search(arr, target):
return binary_search_recursive(arr, target, 0, len(arr) - 1)
# Example usage
sorted_array = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20]
target_element = 12
result = binary_search(sorted_array, target_element)
if result != -1:
print(f"Element {target_element} found at index {result}.")
else:
print("Element not found in the array.")
How It Works
- The
binary_search_recursivefunction takes the sorted arrayarr, target elementtarget, left and right indices of the search interval. - It calculates the middle index (
mid) of the current search interval. - If the element at
midis equal to the target, the indexmidis returned. - If the element at
midis less than the target, the function is called recursively on the right half of the array. - If the element at
midis greater than the target, the function is called recursively on the left half of the array. - The recursion stops when
leftis greater thanright, indicating that the search interval has been exhausted. - The
binary_searchfunction initializes the search interval and calls the recursive function.
Input/Output




Leave a Review