Python Program to Implement Breadth-First Search on a Graph
This Python program implements Breadth-First Search (BFS) on a graph using a queue. BFS is used to traverse or search a graph by visiting all the vertices and edges in breadth-first order, starting from a specified source node.
Breadth-First Search (BFS) is a fundamental graph traversal algorithm that explores all the vertices of a graph in breadth-first order, i.e., it visits all the neighbors of a vertex before moving to their neighbors. BFS is often used to find the shortest path in an unweighted graph and can be employed in various graph-related problems.
Problem Statement
Given a graph represented as an adjacency list, implement the Breadth-First Search (BFS) algorithm to traverse the graph starting from a specified source vertex and print the order in which vertices are visited.
Python Program to Implement Breadth-First Search on a Graph
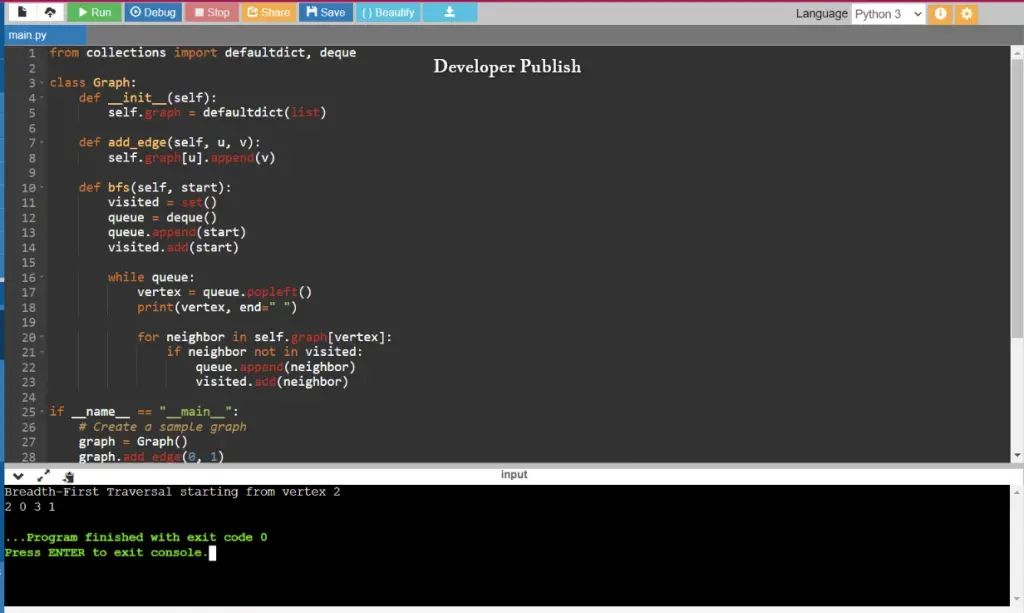
from collections import defaultdict, deque
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
def add_edge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
def bfs(self, start):
visited = set()
queue = deque()
queue.append(start)
visited.add(start)
while queue:
vertex = queue.popleft()
print(vertex, end=" ")
for neighbor in self.graph[vertex]:
if neighbor not in visited:
queue.append(neighbor)
visited.add(neighbor)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Create a sample graph
graph = Graph()
graph.add_edge(0, 1)
graph.add_edge(0, 2)
graph.add_edge(1, 2)
graph.add_edge(2, 0)
graph.add_edge(2, 3)
graph.add_edge(3, 3)
start_vertex = 2 # Specify the starting vertex
print("Breadth-First Traversal starting from vertex", start_vertex)
graph.bfs(start_vertex)
How It Works
- We create a
Graphclass to represent the graph using an adjacency list. - The
add_edgemethod is used to add edges to the graph. - The
bfsmethod performs the BFS traversal. It uses a queue to keep track of vertices to visit and a set to mark visited vertices. - We start BFS from the specified
start_vertex, enqueue it, and mark it as visited. - While the queue is not empty, we dequeue a vertex, print it, and enqueue its unvisited neighbors.
- The process continues until all reachable vertices are visited.
Input/Output




Leave a Review