Python Program to Find Nth Node from End of Linked List
Finding the Nth node from the end of a linked list is a common problem in computer science and programming interviews. This problem tests your understanding of linked list traversal and pointer manipulation
Problem Statement
You are given a singly linked list containing integers, along with a positive integer N. Your task is to find and return the value of the Nth node from the end of the linked list using python.
Python Program to Find Nth Node from End of Linked List
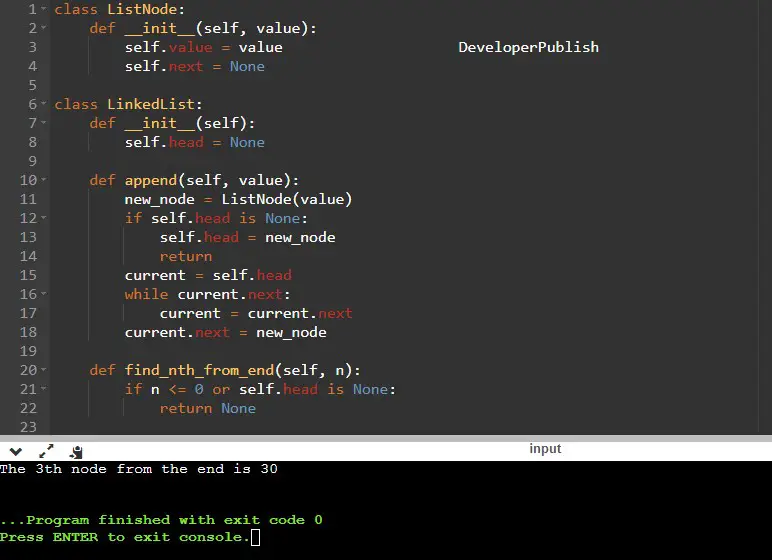
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, value):
new_node = ListNode(value)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def find_nth_from_end(self, n):
if n <= 0 or self.head is None:
return None
slow_ptr = fast_ptr = self.head
for _ in range(n):
if fast_ptr is None:
return None
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next
while fast_ptr:
slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next
return slow_ptr.value
# Example usage
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.append(10)
linked_list.append(20)
linked_list.append(30)
linked_list.append(40)
linked_list.append(50)
n = 3 # Find the 3rd node from the end
result = linked_list.find_nth_from_end(n)
if result is not None:
print(f"The {n}th node from the end is {result}")
else:
print("The linked list is too short.")
How it Works
Step 1: Initialize Pointers We start by initializing two pointers, slow_ptr and fast_ptr, both pointing to the head of the linked list (10).
Step 2: Move Fast Pointer We move the fast_ptr N positions ahead. In this case, we move it 3 positions ahead, so it points to the node with the value 40.
Step 3: Move Both Pointers Now, we move both the slow_ptr and fast_ptr one step at a time until the fast_ptr reaches the end of the linked list (None).
Step 4: Result At this point, the slow_ptr is pointing to the desired node, which is the 3rd node from the end with the value 30.
So, by moving the fast_ptr N positions ahead and then moving both pointers simultaneously until the fast_ptr reaches the end, we can find the Nth node from the end of the linked list efficiently.
Input/ Output




Leave a Review