Using DebuggerDisplay attribute in C#
DebuggerDisplay attribute class in C# lets the developer control on how an object or property needs to be displayed in the debugger variable window.
Assume that you have a class that does not have the DebuggerDisplay attribute to it. For example , Employee class.
public class Employee
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
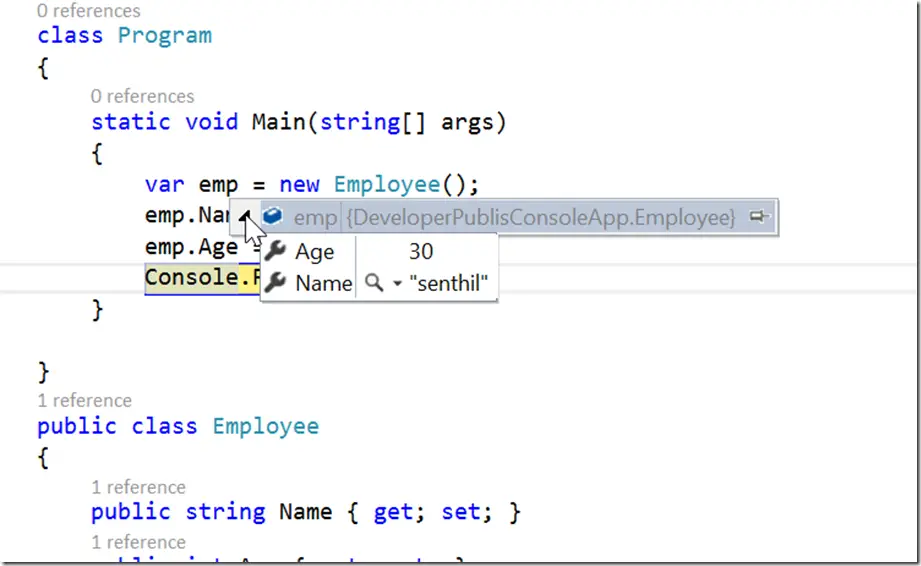
When you create an instance of Employee class and mouse hover on the instance name during debugging , you should see the instance name contains the type name.
In this case , the debugger has used the default type name. Alternatively , you can override the ToString() method so that the Debugger can use it.
The other option is to use the DebuggerDisplay property and when this is used , it takes the priority.
DebuggerDisplay property is useful to view the customized output of the class and display more meaningful text during the debugging.
DebuggerDisplay takes single argument which is a string that needs to be evaluated and this can contain {} or parenthesis which is evaluated as field , property or method.
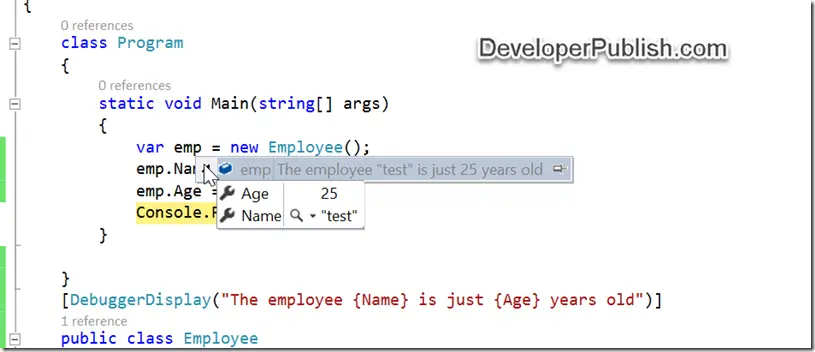
[DebuggerDisplay("The employee {Name} is just {Age} years old")]
public class Employee
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
When you mouse hover on the object when debugging , you will notice a meaningful text as displayed in the screenshot.
Note that the DebuggerDisplay attribute can be applied to types, delegates, properties, fields, and assemblies.


Leave a Review